之前一直以为V8 Pwn是很高深莫测的东西,学了之后发现和PHP Pwn差不多,基本都是通过出题人自己定义的方法上的漏洞进行利用,php pwn是so的拓展,V8是diff文件。当然还有一些直接用CVE出题的
V8基础
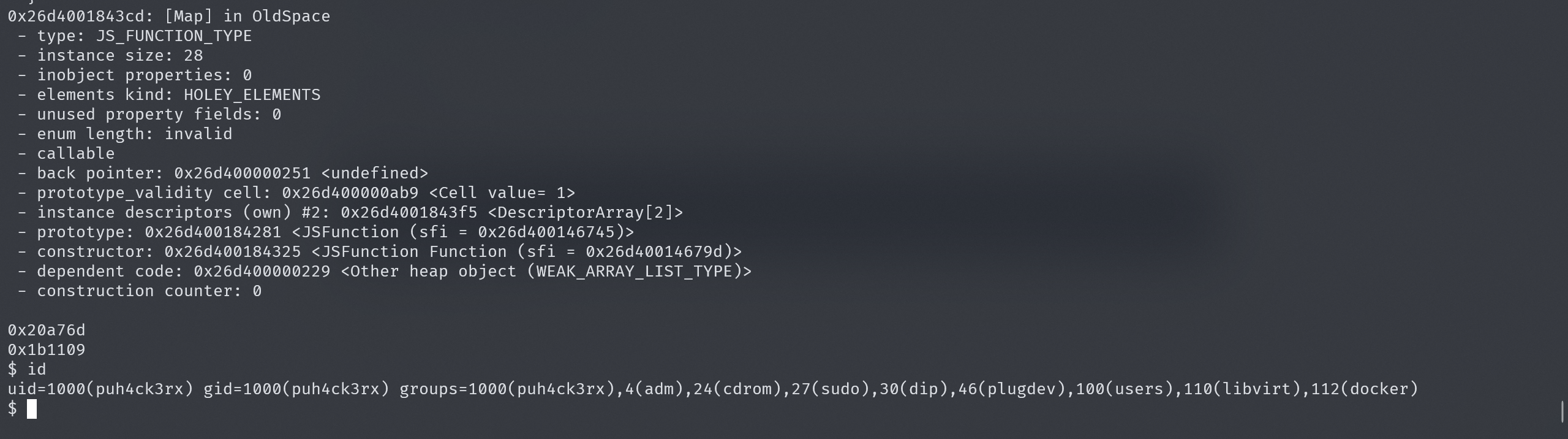
环境搭建和动态调试网上有很多写的很详细,这里就不详细讲了,主要注意一下js 的object的结构体就行
做题时一般出题人会给diff文件和对应的V8版本,退回到之前的版本加上diff文件构建就行
1 | git reset --hard id |
下面记录一下自己刷的V8题
starCTF2019-OOB
1 | fetch v8 |
1 | diff --git a/src/bootstrapper.cc b/src/bootstrapper.cc |
diff文件定义了一个oob方法,漏洞点在将数组元素和数组长度混淆了,导致会溢出1的元素,有点像off by one
oob()无参数时会返回elements[length]的值,带参数时会将参数写入elements[length]
通过调试可以发现float类型和obj类型的数组他们的elements是挨着他们的map的,所以刚好可以泄露map和往map里写数据,这里就可以构造一个类型混淆,通过混淆float类型的数组为obj可以在任意地址伪造一个fake_obj,将obj类型的数组混淆为float可以泄露obj数组储存的对象的地址,那么这样就可以通过自己伪造一个数组然后控制element进行任意地址读写了,最后通过改ArrayBuffer的backing_store的地址 在WasmInstance开辟的rwx内存写shellcode
1 | class Helpers { |
Google CTF 2018 Just-In-Time
这是一道关于Turbon Fan优化的漏洞利用
环境搭建
1 | git reset --hard e0a58f83255d1dae907e2ba4564ad8928a7dedf4 |
下面是patch文件,如果报错可能是windows复制的,换行符转成linux的就行了
1 | diff --git a/BUILD.gn b/BUILD.gn |
漏洞原因
patch在turboFan中的TypedLoweringPhase阶段添加了一种优化方式。
1 | Reduction DuplicateAdditionReducer::Reduce(Node* node) { |
这种优化把x+1+1优化成了x+2,看似不影响,但计算机不是数学,他们的底层不一样
1 | x+1+1应该是 |
而根据浮点数的IEEE764标准 当一个浮点数越来越大时,有限的空间只能保留高位的数据,因此一旦浮点数的值超过某个界限时,低位数值将被舍弃,此时数值不能全部表示,存在精度丢失,下面拿python的来举例

可以看到x+2可以被表示,但x+1不能被表示出来,而checkBounds检测数组越界会在TurboFan的SimplifiedLoweringPhase阶段根据索引和数组的范围被优化,如果索引最大值小于lenth的最小值checkBounds检测将会被优化掉
1 | // Dispatching routine for visiting the node {node} with the usage {use}. |
下面用一个poc来演示一下
1 | function f(x) |

可以看到第一次未被优化时访问的实际时arr[3],强制优化后因为TurboFan认为t最大值是3 Range(2, 3),小于arr的最小值Range(5,5)
所以将checkBounds去掉了,然而patch在SimplifiedLoweringPhase阶段加的优化实际会将t变成5,也就造成了数组越界
可以看到checkBounds在SimplifiedLoweringPhase阶段被优化掉了
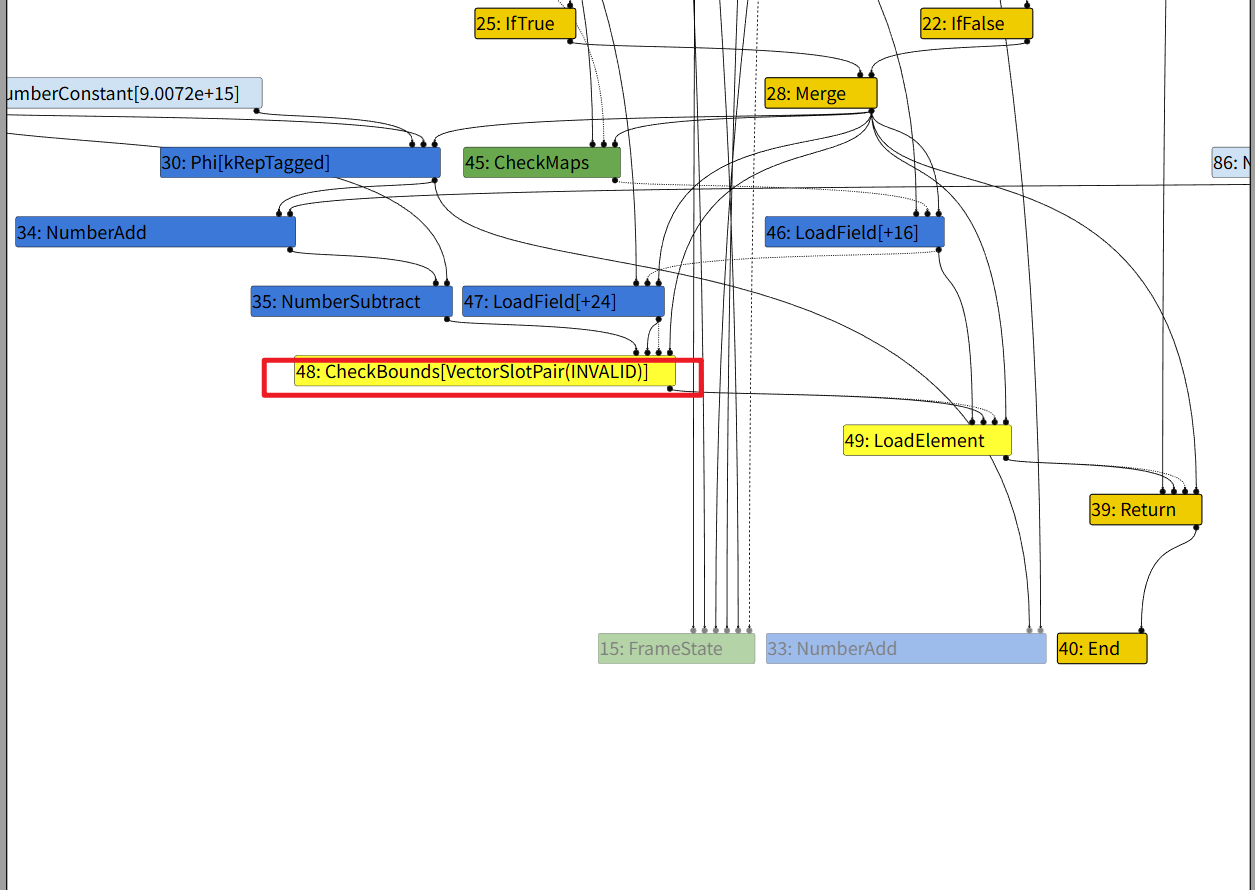
优化掉之前

优化掉之后
具体利用
数组越界感觉可以像上一题那样直接打,但是实际调试下来有%DebugPrint的时候double array obj array的elements确实和map是紧贴的,但是不用%DebugPrint的时候他们之间并不相邻,貌似是%DebugPrint扰乱了内存布局,感觉挺玄学的
1 | class Helpers { |
1 | class Helpers { |
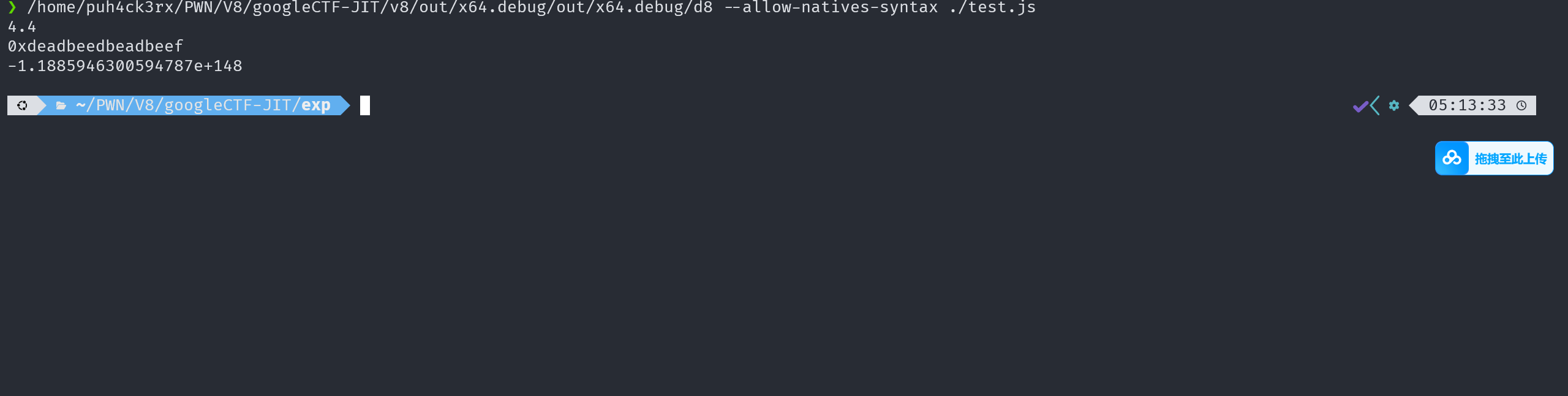
0xdeadbeedbeadbeef肯定不是map,不过测试下来不过 double_arr 的 elements 始终在 obj_arr 的 elements 前面
那么可以通过越界double_arr读出obj_arr的elements,或者通过越界double_arr往obj_arr写一个地址然后通过obj_arr[idx]通过地址伪造出一个对象,也就是实现了addressOf和fakeObject,然后具体越界多少测的时候不能用%DebugPrint直接看elements,因为和实际利用的偏移不一样可以通过%DisassembleFunction(f)获得函数地址然后在在f函数加上一段对elements的操作(也就是访问数组元素),在gdb中断点调试可以根据数组访问元素的相关汇编确定elements的地址然后算出偏移,实际算出是double_arr的idx为18时可以越界到obj_arr[0]
1 | class Helpers { |
解释一下这里f的idx参数因为直接obj_arr[0]会被优化掉导致对象数组不存在(对象数组直接被优化成对象),所以加一个idx可变得值让他不被直接优化成一个对象,但是伪造一个数组进行任意地址读写需要map,调试发现elements附近没有map,也就是刚才的方法用不了,不过目的都是任意地址读写,放一个ArrayBuffer进行调试,可以发现Float64Array有一个类似backing_store的指针存储的位置和double_arr的elements地址接近,查了一下说是backing_store的副本,可以通过越界double_arr来改backing_store指针实现一个任意地址写
1 | class Helpers { |
参考
https://blog.wingszeng.top/2018-google-ctf-just-in-time/
https://kiprey.github.io/2021/01/v8-turboFan/
CVE-2023-4069复现
CVE-2023-4069是关于Maglev图建阶段的一个漏洞 刚好可以用来学习V8中的maglev
环境搭建
1 | git checkout 5315f073233429c5f5c2c794594499debda307bd |
漏洞成因
漏洞主要在Maglev 分配对象中快速路径的部分
下面是分配对象的一个函数示例
1 | Reflect.construct(target, argumentsList[, newTarget]) |
快速路径的分配流程
1 | TNode<JSObject> ConstructorBuiltinsAssembler::FastNewObject( |
条件就是
- new_target的类型是JSFunction
- new_target_func的initial map是否是smi类型,smi指的是低位不是1的地址,因为map在v8中是对象指针,所以低位肯定是1
- target和new_target_constructor相同
- map的类型为DictionaryMap
否则会进入到慢速分配中
diff分析
下面分析一下这个CVE的diff文件,这个diff是修复代码不是以前的制造漏洞的diff,不会真的有人做题时把它patch到v8编译吧
1 | diff --git a/src/maglev/maglev-graph-builder.cc b/src/maglev/maglev-graph-builder.cc |
从这个MaglevGraphBuilder::VisitFindNonDefaultConstructorOrConstruct()函数名不难看出,这个流程发生在Maglev的图建立阶段,用于处理派生类非默认构造函数的访问
1 | if (compiler::OptionalHeapObjectRef constant = |
分析字太多我就懒得打了,而且已经有珠玉在前了 下面给出flyyyy师傅博客上对这段代码的解释,
1 | 首先这里会去判断当前前遍历到的 prototype 对象是不是 JSFunction,接着获取这个function的ref,然后如果当前构造函数有实例字段(或类似需要初始化的成员),就不能跳过这个requires_instance_members_initializer构造函数,必须执行它的初始化逻辑,最后判断当前 class是否 有 private 字段或方法,不存在则会强制执行初始化逻辑 |
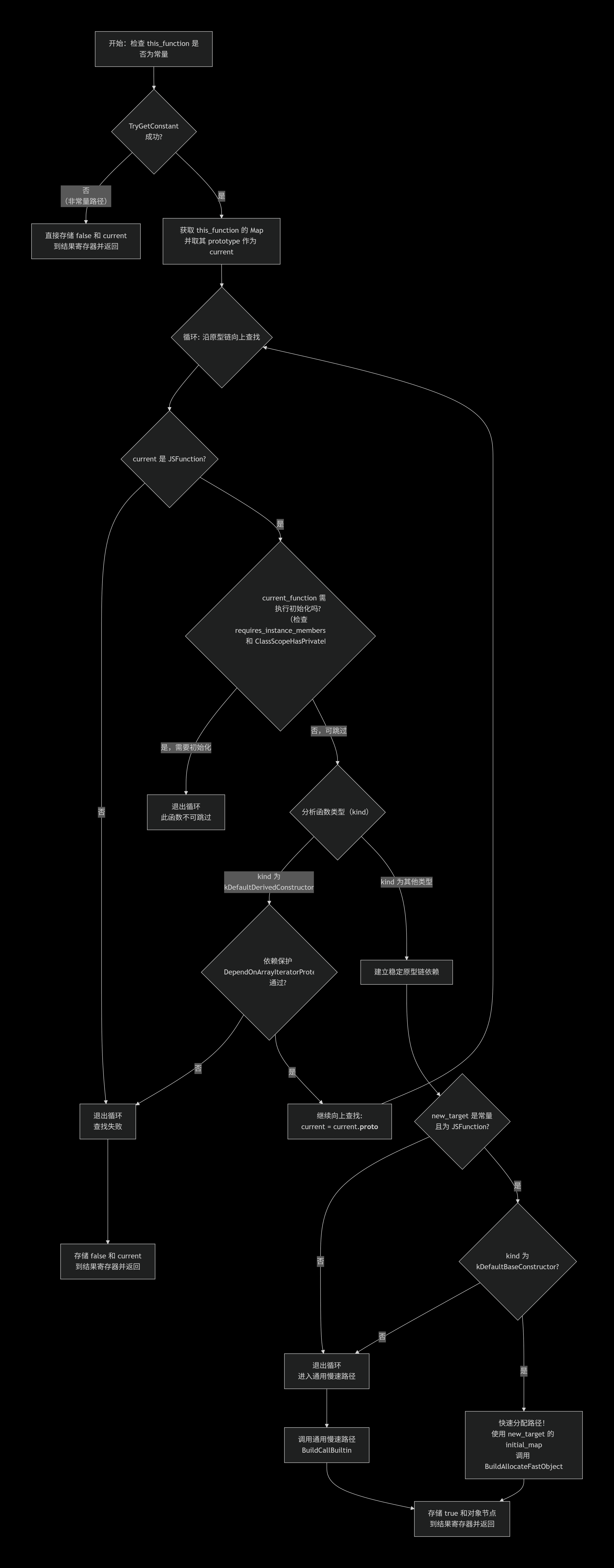
上面的是我让AI根据代码画的一个流程图,也可以看一下这个加速理解
1 | FastObject::FastObject(compiler::JSFunctionRef constructor, Zone* zone, |
然后可以看到这里没有check根据constructor.initial_map来初始化对象的map,也就是base的initial_map,然后根据当前Base的构造函数预测该构造函数实例化对象的最终属性数量和大小,最后就是为这个对象分配内存
可以看出当快速通道走这条路径时并没有检测target与new_target的map的类型是否一致的情况,如果target是JSObject类型new_target是JSArray类型那么就可以造成类型混淆
下面给出根据走上述有漏洞路径的poc
1 | var x = Array; |
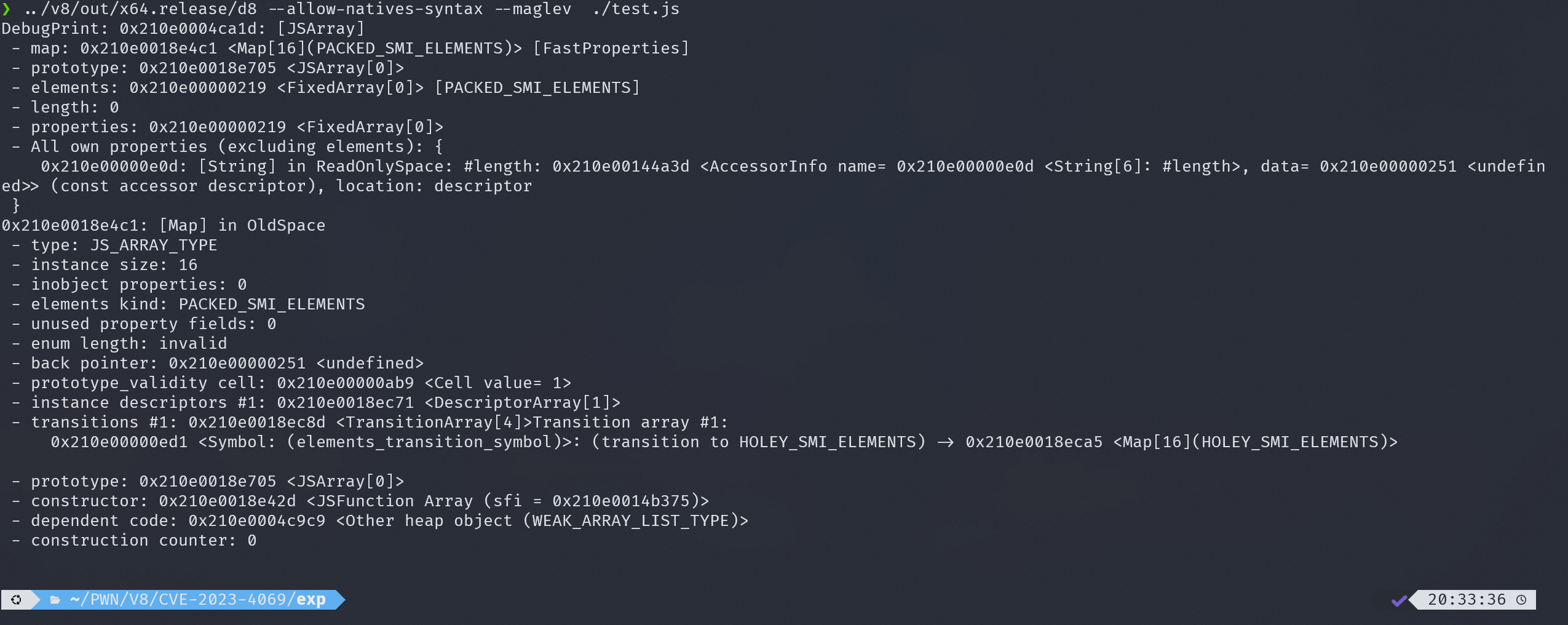
可以看出这里输出了lenth字段,但是由于是通过类型混淆后lenth并没被初始化所以这里是0
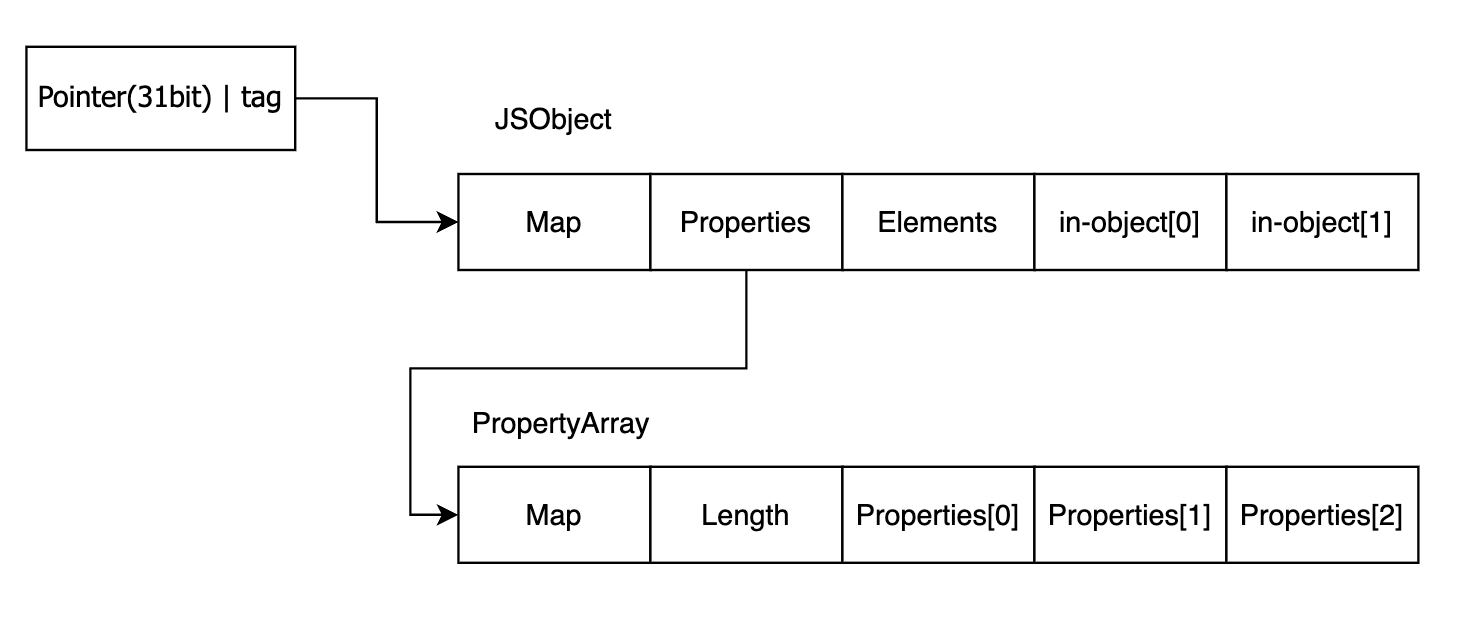
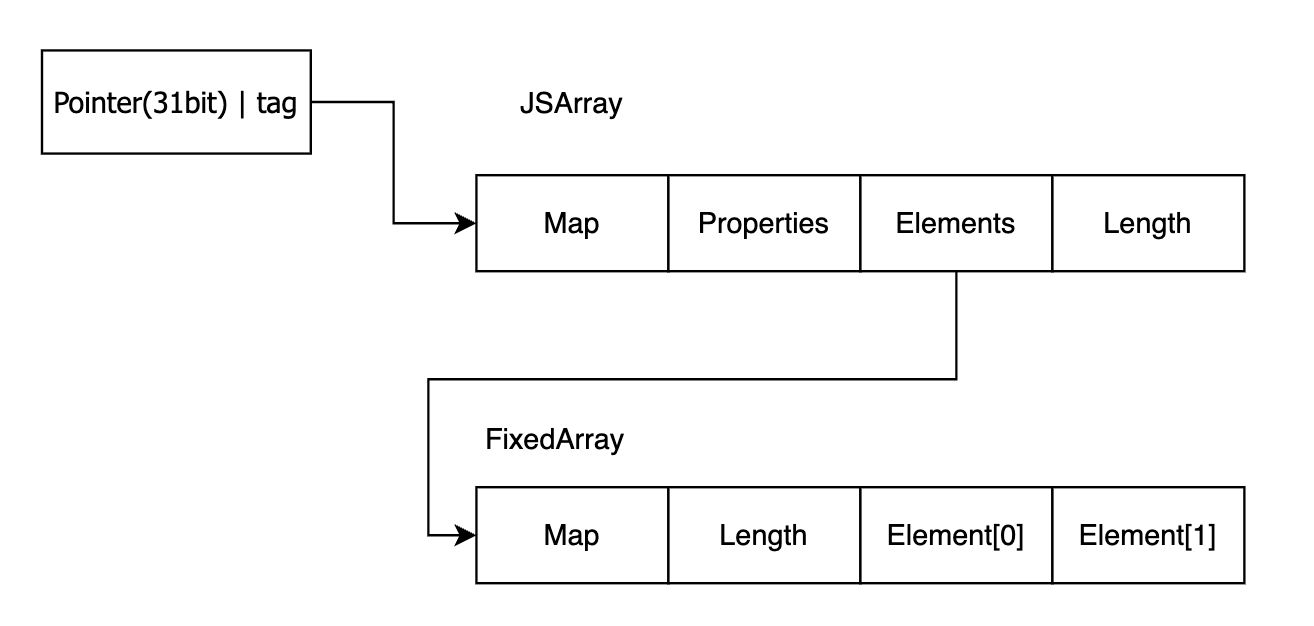
不过可以利用gc回收机制,让分配的对象覆盖到原来可能残留的数据上,又因为lenth并没被初始化,所以lenth区域的残留数据(如果有)是并不会被覆盖的,那么如果lenth刚好是一个很大的值,那么就可以有一个oob了
1 | class Helpers { |
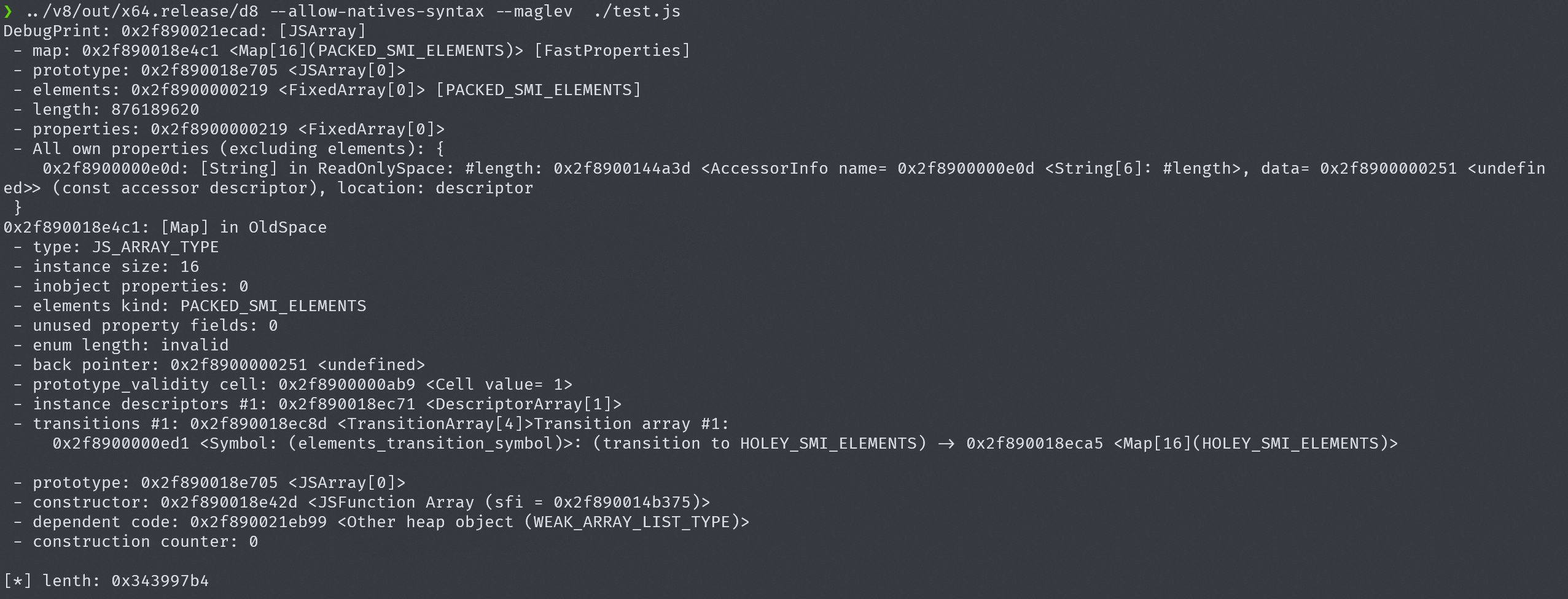
可以看到lenth很大符合我们的要求,通常代码结构不变时lenth处的残留数据值也不变
然后说一下调试时会遇到的问题,写exp调试时可能会加各种输出,这大概率会导致原本的lenth变成很小,或者程序崩溃
这种情况的解决办法就是增多或减少gc()数量,根据笔者调试的经验gc()的数量一般在2-5之间,这种问题目前遇到的debug输出或者改变代码结构,哪怕一行都会出现,所以调试时每次代码结构改变都得重新设置gc()数量
exp编写
笔者当时的想法是直接oob读出map类型混淆,实测时发现如果oob的读一些地址会直接崩溃掉,可能是地址不稳定造成的?
1 | var oob_array = construct(); |
下面参考了flyyyy师傅的方法利用Heap Spary在堆上喷一个victim_array,因为Heap Spary victim_array相对oob_array的地址比较稳定
然后就去伪造一个map以及fakeobject进行任意地址读写,最后JIT Spary执行shellcode 不过实际测试下来因为Heap Spary所以map的地址也基本稳定,所以可以不伪造map也行
1 | class Helpers { |
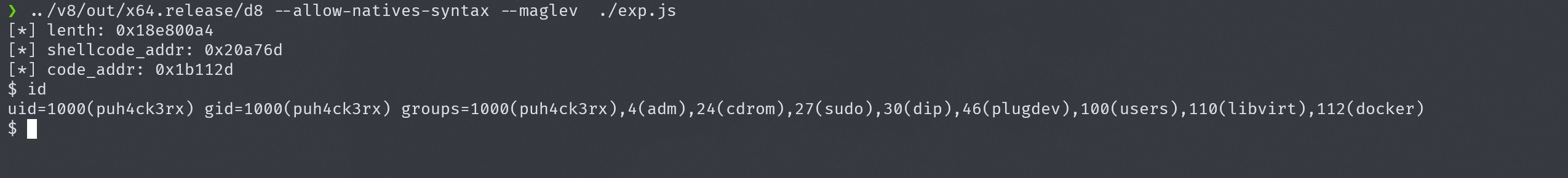
下面不伪造map也可以getshell
1 | class Helpers { |